Cobalt is a metal that has been used for centuries for colouring ceramics and glassware. In the 20th century, cobalt began to be used increasingly in modern technologies such as aircraft turbines due to its high wear resistance, high temperature strength and unique magnetic properties. It is now highly in demand for the use in lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles and portable devices such as mobile phones.
The electric vehicle market is developing rapidly. The International Energy Agency forecasts that there will be 200 million electric vehicles on roads across the globe by 2030, which translates to a cobalt demand growth for electric vehicle batteries from 160 000 tonnes in 2021 to 250 000 tonnes in 2030. Despite considerable efforts to reduce the cobalt content in batteries due to its high price and supply risks, it is difficult to substitute its unique properties and it is likely to play an important role in the battery technologies of the near future.
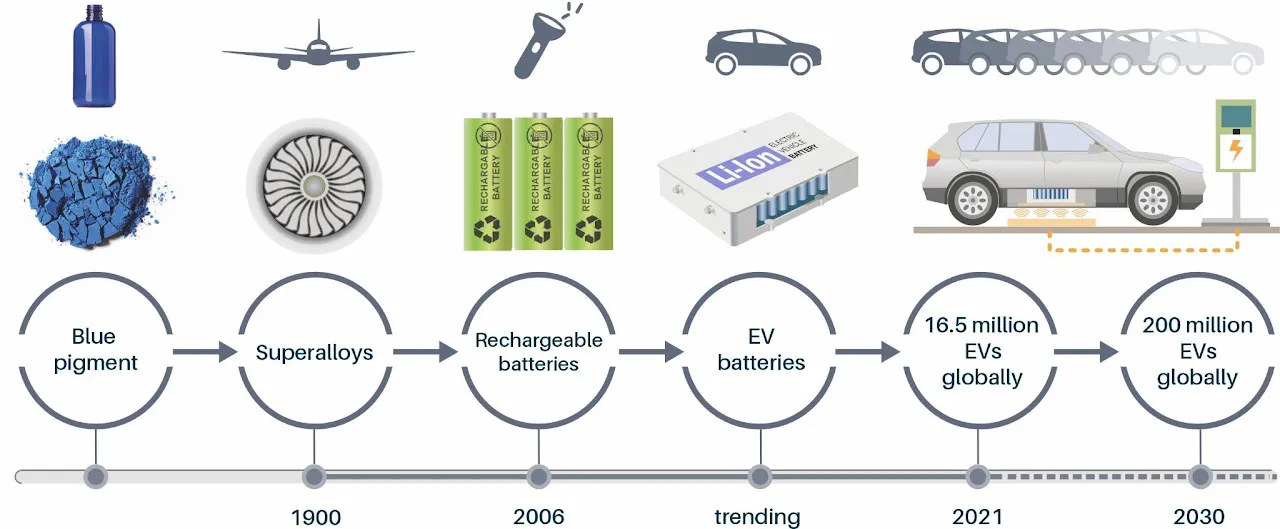
The second-largest use of cobalt is in batteries for portable devices. Such devices chiefly use batteries with a high cobalt content (lithium-cobalt oxide chemistry with 89 per cent cobalt) that have a high energy density and give them a long run-time. Cobalt is also used in many other applications, including various alloys such as superalloys for the aerospace industry and in hard metals (cemented carbide) for hard-wearing cutting and grinding tools. It is also used as a catalyst in oil and gas refinineries to remove sulphur and it is still used for colour pigments in ceramics, enamels, inks and glass, for which it has been used since antiquity. Other uses include magnets for wind turbines and motor sensors, hard facing, energy storage, tyres, soaps and paint driers.
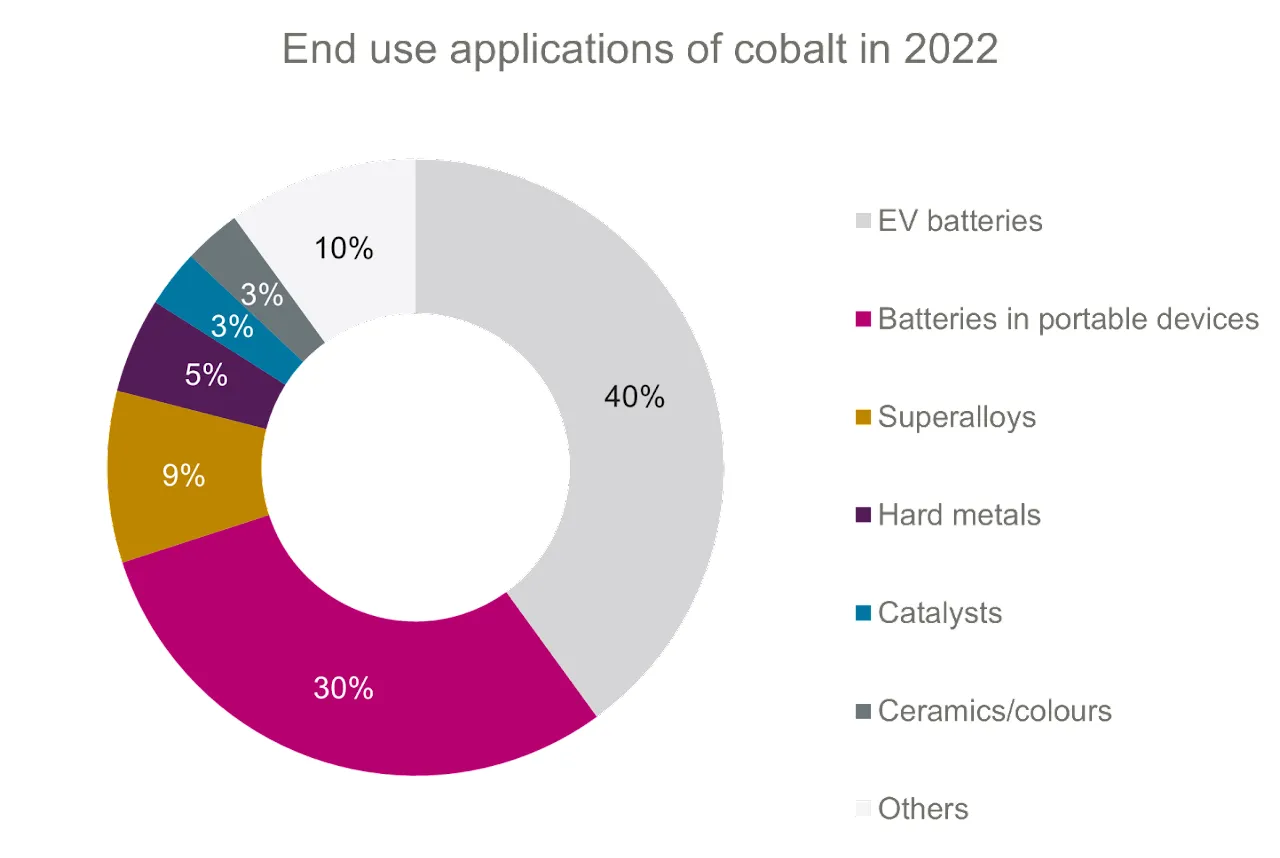
Acquiring cobalt
Supply chain
Cobalt is mainly produced as a by-product of copper from sediment-hosted copper/cobalt deposits, most of which are found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) in central Africa. The second-largest production of cobalt comes from nickel mining (laterite and magmatic sulphide deposits), where the main producers are Australia and Indonesia.
Cobalt is traded in a variety of different products that are used for different manufacturing purposes. Cobalt from the DRC is chiefly processed into cobalt hydroxide, while other operations produce other cobalt chemicals (for example, cobalt sulphide) and cobalt metal. Most of these intermediate products are shipped to China, where it is further refined to a product that is used in manufacturing for various applications. Cobalt sulphate is the main product that is used to manufacture battery cathodes.
Exploration
Cobalt has become a popular exploration target due to the need for new sources of this key battery raw material. The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that global cobalt demand will increase from 160 000 tonnes in 2021 up to 250 000 tonnes per year in 2030 (IEA, 2022). Exploration projects are widely distributed across the globe, with rapid developments of several new projects, especially in Indonesia (Cobalt Institute, 2023b).

There are several different deposit types that can contain and extract cobalt, with three types accounting for about 85 per cent of terrestrial global cobalt resources (Mudd and Jowitt, 2018):
- magmatic nickel-copper-cobalt (with or without platinum-group elements (PGEs)) sulphides
- stratiform, sediment-hosted copper-cobalt
- nickel-cobalt laterite deposits
Cobalt is usually a by-product of these deposits, as the main commodities are chiefly copper or nickel. Other target commodities include gold, PGEs and silver.
Magmatic nickel-copper deposits are an important source of nickel, with nearly 40 per cent of world production in 2017. Major deposits are located in Russia, Canada and Australia. Stratiform sediment-hosted copper-cobalt deposits are the main source for cobalt, mainly extracted from the Central African Copperbelt in the DRC and Zambia. Large deposits of this type also occur in Europe (Kupferschiefer) and Russia (Udokan Basin), but cobalt concentrations are much lower and copper is the main commodity.
| Deposit type | Description | Typical size (Mt ore) |
Co-bearing minerals | Examples (with Co ore grade) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magmatic Ni-Cu-(Co-PGE) | Massive to disseminated sulphides hosted in mafic to ultramafic igneous rocks | 5 to >500 |
|
|
| Stratiform sediment-hosted Cu-Co | Hydrothermal sulphide deposits loosely bound to a siliciclastic or carbonaceous unit(s) | 10 to 500 |
|
|
| Ni-Co laterite | Supergene weathering products of mafic to ultramafic rocks | 10 to 800 |
|
|
| Black-shale hosted | Disseminated sulphides in dominantly sulphur-rich black shales | Very large mineable deposits (1525 Mt at Sotkamo) |
|
|
| Metasediment-hosted Co-Cu-Au | Massive to disseminated sulphides in stratabound zones, lenses, veins, breccias; mainly in rift-related environments | <1 to 31 |
|
|
| Polymetallic Co-rich veins | Hydrothermal sulphide veins; some known as 'five element vein' deposits (Ni-Co-As-Ag-Bi) | <20 |
|
|
| Iron-oxide Cu-Au (Ag-U-REE-Co-Ni) (IOCG) | Magmatic (?)-hydrothermal, structurally-controlled replacement deposits; usually in an intracratonic setting | 5 to >9 000 |
|
|
| Volcanogenic massive sulphide (VMS) | Massive sulphides formed in a submarine volcanic environment; cobalt concentrations may be high where hosted in ultramafic to mafic rocks | <10 to 300 |
|
|
| Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) | Epigenetic hydrothermal deposits hosted typically in dolostone or limestone; cobalt is rarely enriched | 7 (median deposit size)* |
|
|
| Skarn and replacement deposits | Sulphides associated with calc-silicate minerals | 100 to 500 |
|
|
Reserves of cobalt
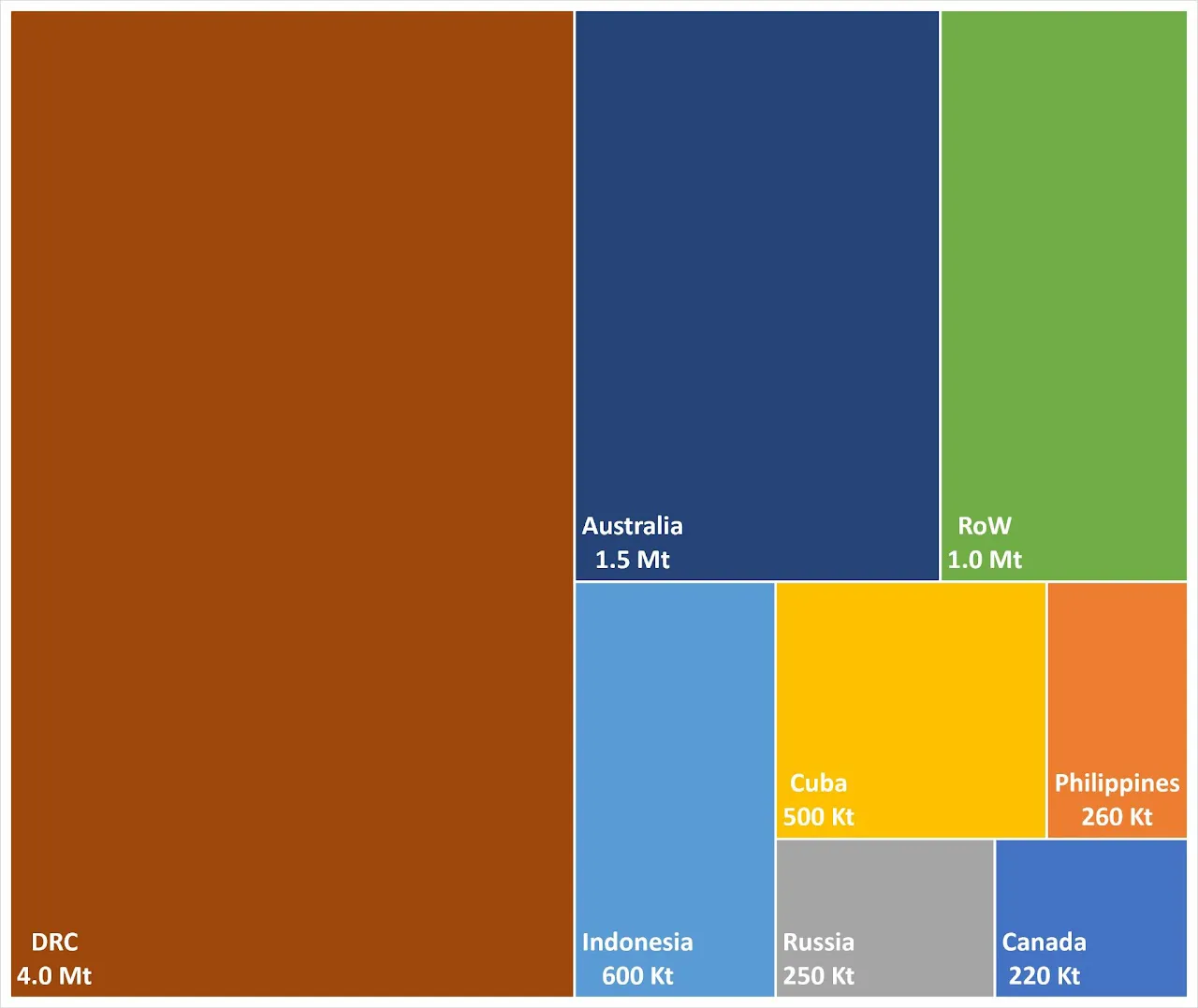
Cobalt reserve data from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) indicate a total of 8.3 million tonnes of cobalt, with almost 50 per cent situated in the DRC in sediment-hosted copper-cobalt deposits.
Australia also contains a significant proportion of cobalt reserves in magmatic nickel-copper deposits as well as nickel-cobalt laterite deposits; there are also substantial investments into new exploration projects concerning cobalt.
Indonesia currently holds the third-largest reserves, with many new nickel-cobalt laterite deposits being developed in the last few years that plan to produce cobalt as a by-product.
Extraction
Cobalt is chiefly extracted as a by-product of copper and nickel. Mine production is dominated by the DRC, which produced 71 per cent of the world's cobalt in 2021 (93 011 tonnes). Deposits in the DRC are sediment-hosted stratiform copper-cobalt deposits, where it is concentrated and mostly processed into cobalt hydroxide. While most of this is extracted from large-scale operations, roughly 15 to 30 per cent of cobalt from the DRC is extracted in artisanal and small-scale mining, which can be linked to child labour and poor working conditions.
Russia and Canada are producing cobalt from magmatic nickel-copper-cobalt sulphide deposits; Cuba produces cobalt from its nickel-cobalt laterite deposits, whilst Australia has both magmatic sulphide and laterite deposits from which it extracts cobalt.
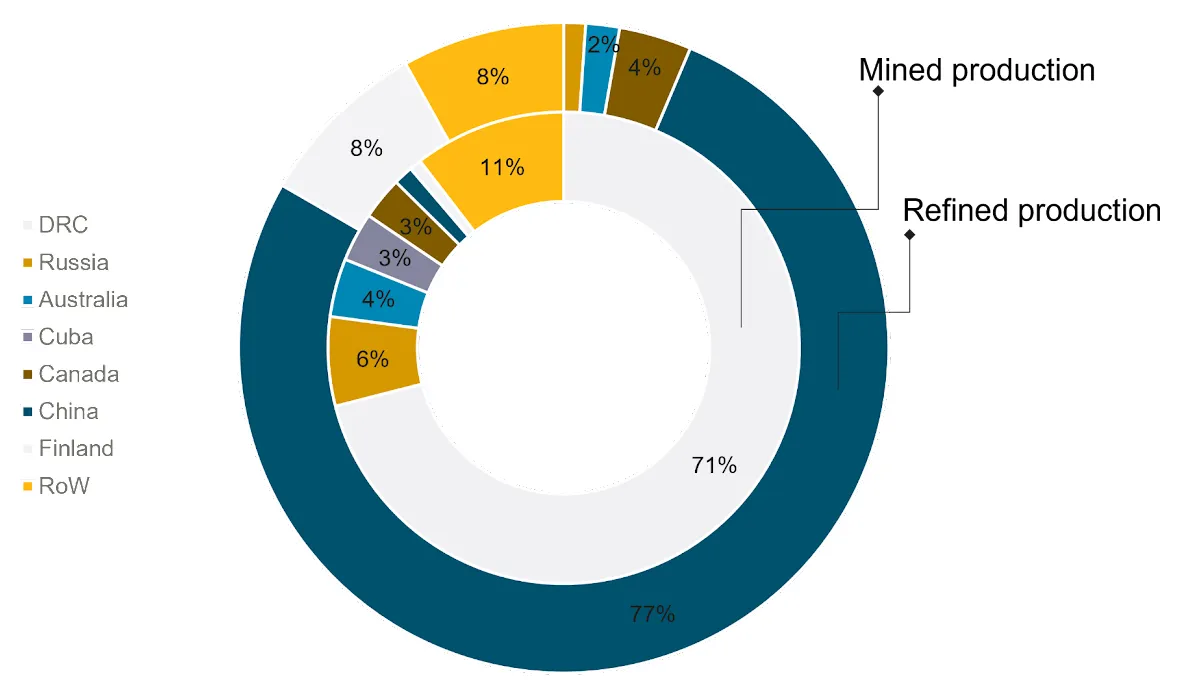
Despite only a small cobalt mine production in China, the country is the main refiner of cobalt with 71 per cent in 2021. Cobalt is dominantly imported as cobalt hydroxide from the DRC but imports from from laterite projects as nickel-cobalt mixed hyroxides in Indonesia are increasingly rapidly. China has large shares in the majority of the DRC operations and has increased its investment in Indonesian laterite projects in the last years (Cobalt Institute, 2023b). Thus, China controls a large part of the early cobalt supply chain. Other important refining countries are Finland, Canada and Australia.
Processing
The vast majority of cobalt ores are first crushed and milled to a finer grain size, so that the cobalt-bearing minerals can be easily separated from surrounding rock and other minerals of no economic interest. Further concentrating and processing of cobalt depends on the type of ore. The main sources of cobalt are three different deposit types:
- sediment-hosted copper-cobalt deposits
- nickel-cobalt laterite deposits
- magmatic nickel-cobalt deposits
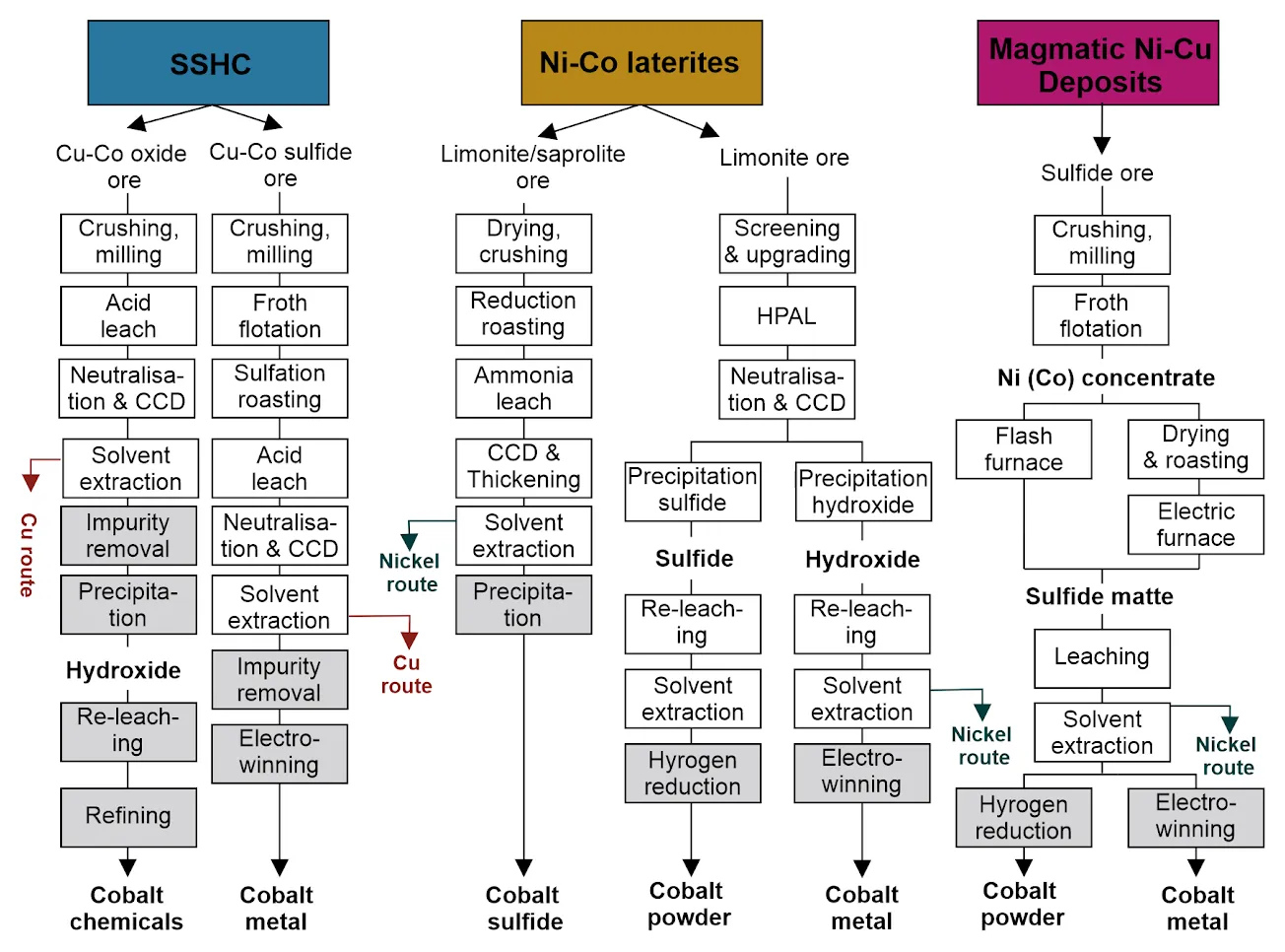
Sediment-hosted copper-cobalt deposits
Sediment-hosted copper-cobalt deposits are mined and processed in the DRC and Zambia and generally produce copper, with cobalt as a by-product. There are two different ore types, sulphide and oxide ores, which can be treated in different ways to reach the best metal recoveries.
Oxide ore is commonly treated by whole-ore leaching (WOL), where the minerals are dissolved in acid. Subsequently, solvent extraction is used to separate the copper and cobalt and remove impurities. Sulphide ores are first concentrated by froth flotation and roasting before leaching, solvent extraction and impurity removal. Final precipitation commonly produces a cobalt hydroxide, but electrowinning can also be used to produce pure cobalt metal.
Nickel-cobalt laterite deposits
Laterite deposits generally consist of two different ore types: saprolite (silicate-dominated)and limonite (oxide-dominated). The ratio between the two in a single deposit determines the best processing technologies for optimal recovery.
Saprolite ore is chiefly smelted to produce ferronickel, which is used in the stainless steel industry, and cobalt is not recovered during this process.
High-pressure acid-leaching (HPAL) is the most popular processing route for deposits that chiefly contain limonite ore, as the recovery rates for nickel are higher. Cobalt is also recovered with recoveries of more than 90 per cent for both metals. After leaching of the ore in an autoclave under high pressure and temperature, and additional steps to remove impurities, a mixed nickel-cobalt sulphide or hydroxide is precipitated; this can be a sellable product on its own, or it can be re-leached to produce a pure cobalt powder via hydrogen reduction or cobalt metal via electrowinning.
HPAL is used in Murrin Murrin, Australia, and new operations in Indonesia. An alternative is the Caron process, where both limonite and saprolite ore can be treated together by roasting and subsequent ammonia leaching of the ore. However, overall recoveries are lower than in HPAL plants and decrease with higher contents of saprolite ore. This process is used in active operations at Punta Gorda, Cuba.
Magmatic nickel-copper (cobalt-platinum-group elements) deposits
In magmatic nickel-copper sulphide mines, copper is generally separated from nickel and cobalt via flotation and the resulting nickel-cobalt concentrate is processed by smelting in a flash furnace or electric furnace. The resulting sulphide matte is then leached, followed by solvent extraction to recover nickel and cobalt. The overall recovery of cobalt is relatively low at only 40 per cent and depends strongly on the dominant mineral host of cobalt. Current operations that undergo this pyrometallurgical processing route are Sudbury, Canada, and Norilsk, Russia.
Drivers and alternatives
Secondary sources
Secondary sources can form an important part of the future cobalt supply, as large quantities of cobalt end up in waste streams at different stages in the value chain. As cobalt is mainly a by-product of copper and nickel production, metallurgical processing routes are not optimised for cobalt recovery and a significant proportion ends up in mining wastes. Manufacturing waste (new scrap) can be recirculated to ensure more efficient use of cobalt components. However, the largest secondary future cobalt resource is most likely end-of-life (EOL) products, particularly lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles, which will gradually become more available for recycling.
Mining and refining waste
In many mining operations, cobalt is not prioritised for recovery as it only makes up a small proportion of the revenue compared to the main commodities of copper or nickel. It is estimated that between 40 and 60 per cent of cobalt is lost during ore processing to make a concentrate. Equally, smelting of sulphide ores from magmatic nickel-copper-cobalt sulphide deposits only recovers roughly 60 per cent of cobalt, but 80 per cent of nickel. The remainder will end up in the waste streams in mine tailings or as slag from smelting. There are several projects in central Africa that attempted to recover cobalt from tailings (Petavratzi et al. 2019). A successful example is the Kasese project in Uganda, which recovered cobalt from pyrite-rich mine tailings via a bioleaching process on an industrial scale. The facility produced 800 tonnes of cobalt per year from 1998 to 2014 (BRGM, 2023).
Another study at Nkana, Zambia, investigated the reprocessing of slag to produce a cobalt-rich alloy that can be further refined into cobalt metal. The Nkana site contains 20 million tonnes of slag with an average cobalt content of 0.76 per cent, higher than cobalt grades in many cobalt-producing mines. However, the process was never fully implemented and the operator decided to use a less expensive technology with no cobalt recovery (Petavratzi et al. 2019).
Recycling
The IEA forecasts that the amount of spent lithium-ion batteries will surge after 2030, with 1 TWh reaching their end of life by 2040 (SDS scenario) (IEA, 2021). An electric vehicle battery contains between 5 and 33 per cent cobalt (amongst many other valuable materials). Successful recycling depends on the collection of end-of-life products, battery types and cobalt prices. Battery recycling involves mechanical recovery, pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy or a combination of the three. Recycling efficiency of cobalt from lithium-ion batteries are relatively high at more than 85 per cent (Tkaczyk et al. 2018).
Other important waste streams include scrap from superalloys and nickel-cobalt alloys, as well as catalysts. These are often recycled in existing or secondary smelting facilities (pyrometallurgy). Spent cemented carbide (cobalt-bearing hardwearing tools) can be recycled via the zinc method and produce cobalt metal powder (Petavratzi et al. 2019).
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) estimates an overall end-of-life recycling rate of 68 per cent cobalt, but the recycled content in newly fabricated cobalt metal is only 32 per cent (UNEP 2011).
The main challenges to increase cobalt recycling are:
- economics of the scrap material, that is, the presence of other valuable materials and uncertainty material composition, making large-scale and efficient recycling difficult
- poor end-of-life collection rates, which affects the viability of the recycling sector
- hibernating stocks of, for example, consumer electronics, and lack of consumer engagement associated with waste management
(Petavratzi et al. 2019)
More information
References
BRGM. 2023. 1995 — BRGM and the KCC project. [Accessed: 19/01/2023]
Cobalt Institute. 2023a. Cobalt Market Report 2022 (pdf).
Cobalt Institute. 2023b. Essential cobalt.
Dehaine, Q, Tijsseling, L T, Glass, H J, Törmänen, T, and Butcher, A R. 2021. Geometallurgy of cobalt ores: a review. Minerals Engineerin, Vol. 160, 106656. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106656.
IEA. 2021. The role of critical minerals in clean energy transitions — world energy outlook special report (pdf).
IEA. 2022. Global EV Outlook 2022 — securing supplies for an electric future.
Lusty, P A, Josso, P, Price, F, Singh, N, Gunn, A G, Shaw, R, Deady, E A, Grant, H, and Idoine, N E. 2022. Study on future UK demand and supply of lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese and graphite for electric vehicle batteries (pdf). British Geological Survey Commissioned Report CR/22/079. (Nottingham, UK: British Geological Survey.)
Mudd, G M, and Jowitt S M, 2018. Growing global copper resources, reserves and production: discovery is not the only control on supply. Economic Geology, Vol. 113, 1235&nbdash;1267. DOI: 10.5382/econgeo.2018.4590
Petavratzi, E, Gunn, A G, and Kresse, C. 2019. Cobalt. BGS Commodity Review.
Tkaczyk, A H, Bartl, A, Amato, A, Lapkovskis, V, and Petranikova, M. 2018. Sustainability evaluation of essential critical raw materials: cobalt, niobium, tungsten and rare earth elements. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Vol. 51, 203001. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/aaba99
Further reading
Horn, S, Gunn, A, Petavratzi, E, Shaw, R, Eilu, P, Törmänen, T, Bjerkgård, T, Sandstad, J, Jonsson, E, and Kountourelis S 2021. Cobalt resources in Europe and the potential for new discoveries. Ore Geology Reviews, Vol. 130, 103915. DOI: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103915